Lebanon’s location bordering Syria made it a trading hub between the Mediterranean and Arab worlds and resulted in it becoming the most religiously diverse country in the Middle East. Its mountains isolated religious and ethnic groups from each other.
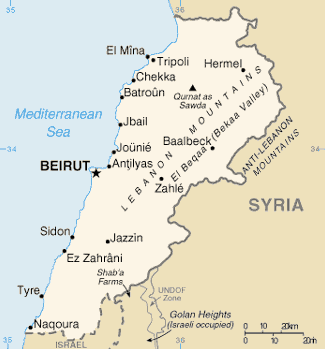
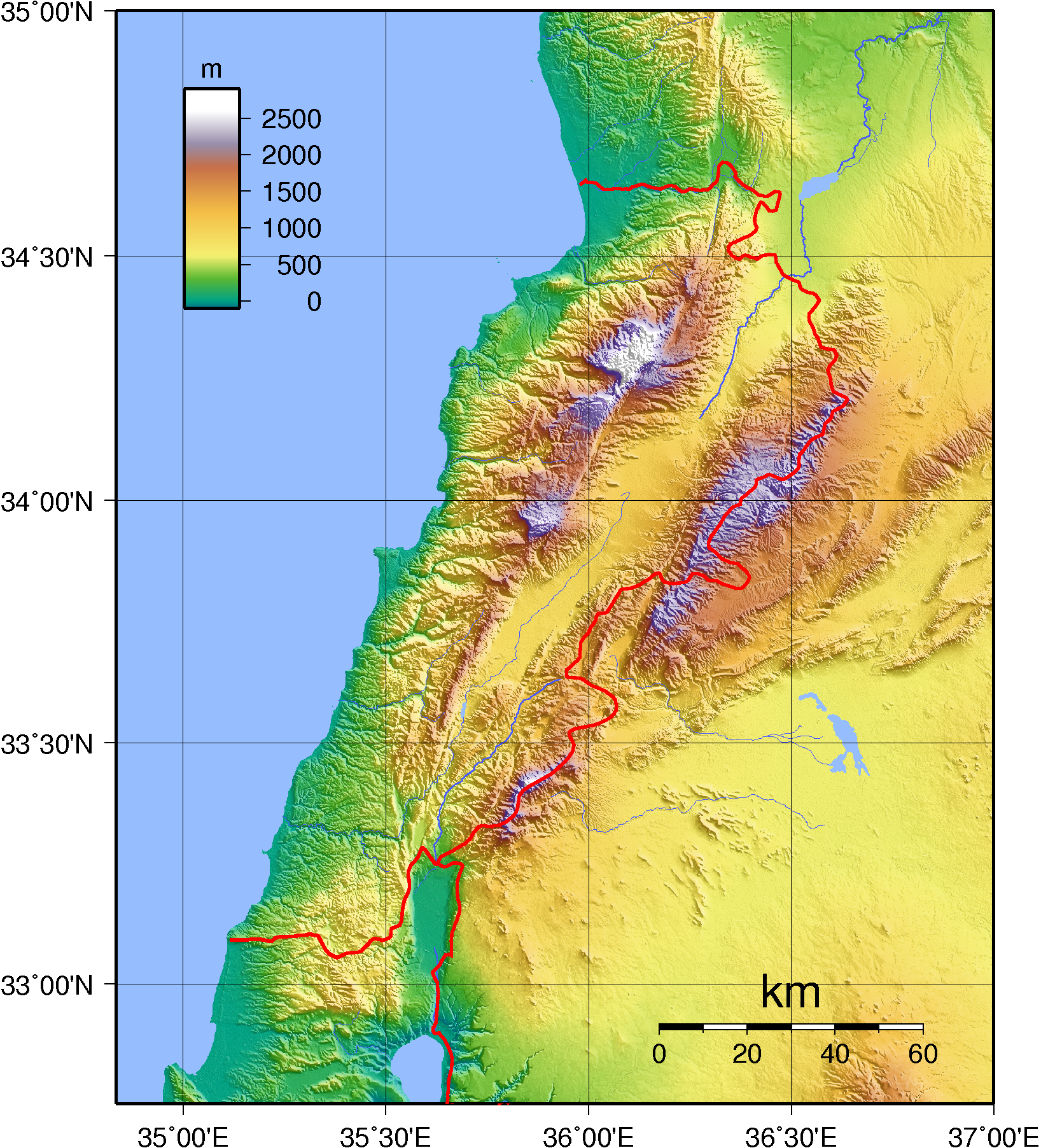
Lebanon is north-south alternating strips of lowland and highland–a coastal plain, a mountain range, a central plateau, then more mountains. Its shoreline is regular, rocky and has no deep harbor. The Beqaa Valley between the mountain ranges is the main agricultural area but fruit and vegetables grow well on the very narrow maritime plain.
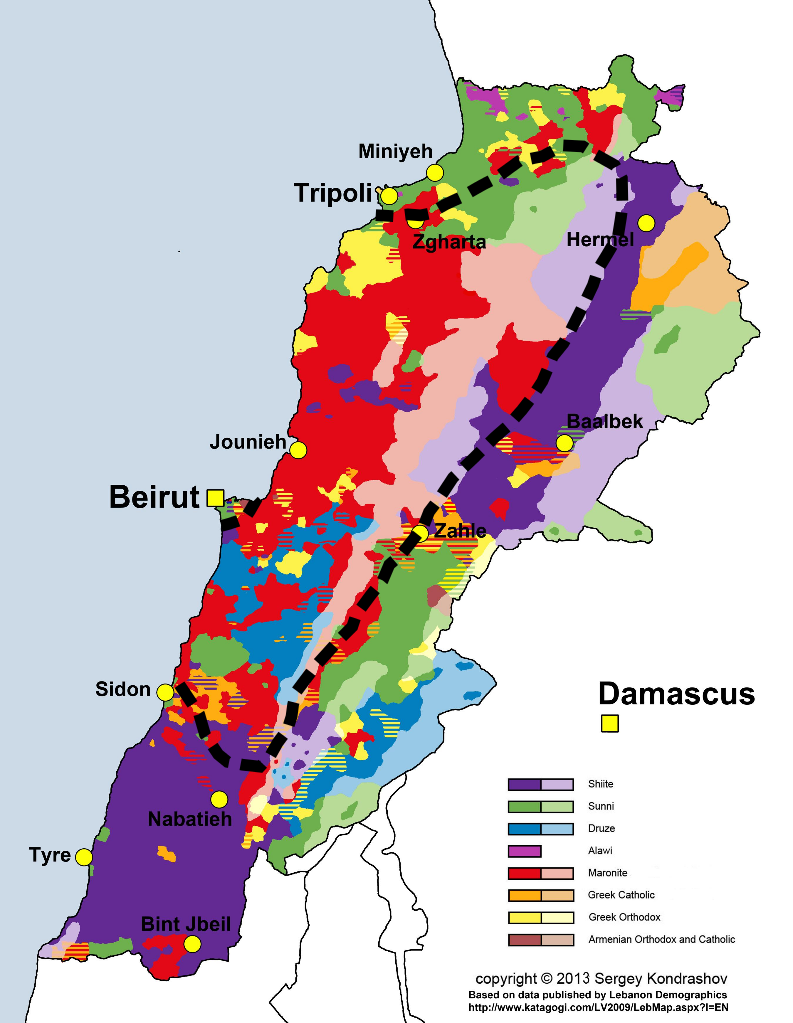
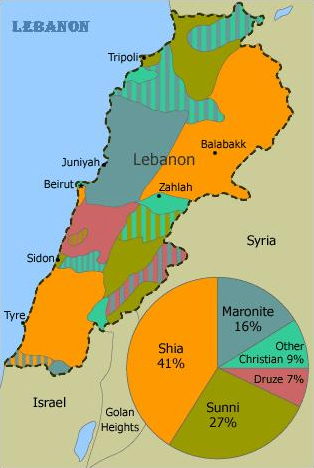
The CIA estimates the population to be 40% Christian, 27% Shia, 27% Sunni, and 5% quasi-Shia Druze. The Lebanese Information Center estimates 34% Christians while Statistics Lebanon estimates 46% Christian. The 34% to 46% range for Christians is matched by a 27% to 40% range for Shia.
There are several Christian groups. Maronite Catholics make up 21% of the overall population, Greek Orthodox 8%, Greek Catholic 5%, Protestant 1% and 6% other denominations. When the last census was taken in 1932, Christians were 53% of the total. It was about the same in 1956 but more Christians than Muslims have emigrated since then and the Muslim population has a higher birth rate.
Lebanon has over thousands of years been part of many empires. It became an orthodox Christian center under the Romans. They persecuted an ascetic Christian tradition established near Mount Lebanon in the late 4th century by a hermit named Maron. Most of Lebanon was ruled as a Christian Crusader State from 1109 to 1289.
Most eastern Mediterranean Christian communities swore allegiance to the head of Eastern Christianity in Constantinople, but the Maronites aligned with the Pope in Rome, which led to centuries of support from France and Italy even after Lebanon became part of the Ottoman Empire in 1516.
In 1842, fighting between Maronites and the Druze led to the Mount Lebanon area being separated into a Christian district in the north and a Druze one in the south, both of which reported to the governor of the Sidon district in Beirut. France got the northern district separated entirely from Muslim Syria in 1861 to protect Mount Lebanon’s 80% Christian population
In 1920, after the Ottoman Empire fell, the League of Nations gave Syria and Lebanon to France, and Palestine and Iraq to Britain. France was welcomed by Christians around Mount Lebanon and vehemently rejected by Muslims in Syria. It took until 1923 for France to gain full control.
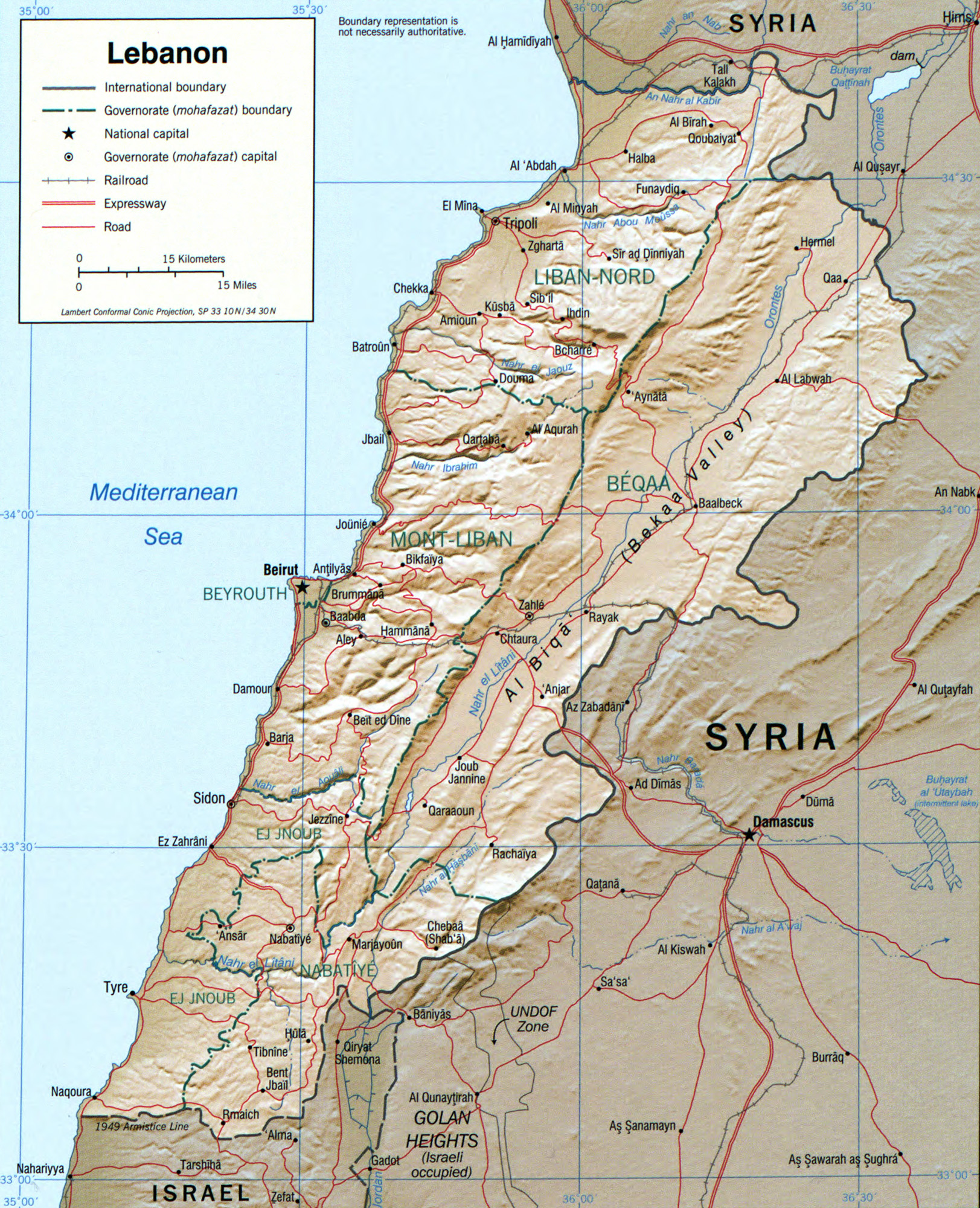
France added Tripoli, north of which is primarily Sunni, to the former Ottoman district of Mount Lebanon, along with Sidon, south of which is chiefly Shia, and the Bekaa Valley, which has a mix of Muslims, Christians and Druze, and established it in 1926 as the democratic republic of Lebanon.
A political system was established that shares power based on religious communities. There is an unwritten agreement that the president will be Maronite Christian, the speaker of the parliament Shia, the prime minister Sunni and the Deputy Speaker of Parliament and the Deputy Prime Minister Greek Orthodox. The Shia have considered themselves marginalized ever since. They as well as the Maronites were persecuted by the Ottomans.
When France’s puppet government during WW2 allowed Germans through Syria to attack British forces in Iraq, Britain invaded Syria and Lebanon. France then said Lebanon would become independent with France’s ongoing support. But when the newly elected Lebanese government abolished France’s mandate in 1943, France imprisoned them. France was then forced by international pressure to recognize Lebanon as fully independent. France withdrew its troops in 1946.
In 1958, Muslim demands for reunification with Syria led to the brink of civil war and US military intervention when Muslims wanted Lebanon to join the newly formed Egyptian-Syrian United Arab Republic. Tension with Egypt had been growing since 1956 when Lebanon’s Christian president did not break with Israel and the Western powers that attacked Egypt to regain control of the Suez Canal.
Internal tensions continued to grow. In 1975, civil war broke out between a Christian coalition and an alliance of Druze and Muslims with the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO). Syria sent troops, allegedly for peace-keeping, that remained in Lebanon until 2005, long after the end of the war.
The PLO leaders had set up new headquarters in Beirut after they lost the 1970-71 civil war with the Sunni monarchy for control of Jordan. The PLO was founded in 1964 in Jordan where Palestinian refugees from Israel had become the majority population.
Thousands of Palestinian fighters fled to Lebanon after the Syrian civil war, preceded by refugees from Israel and followed by more from Jordan. There are 450,000 Palestinian refugees in Lebanon now, primarily in the south.
In 1978, Israel invaded southern Lebanon to push PLO forces away from the border.
In 1982, PLO attacks led to a second Israeli invasion through Shia southern Lebanon and a siege of Shia Beirut. The militant Shia political party Hezbollah came into being in the next few years to expel Israel forever and end Shia marginalization.
The civil war ended in 1990 with an agreement to disband all non-governmental Lebanese militias and deploy the Lebanese army on the border with Israel. But Syria’s Shia government, which controlled Lebanon then, with fundamentalist Shia Iran’s support, allowed Hezbollah to continue fighting a guerrilla war against Israel and the South Lebanon Army in Shia areas occupied by Israel until 2000. Many see Hezbollah as a proxy of Syria and Iran.
Hezbollah has continued fighting with reduced intensity since then to liberate Shebaa Farms in the Golan Heights, territory occupied by Israel since 1967. The UN considers Shebaa Farms Syrian territory. Both Syria and Lebanon consider it part of Lebanon. UN resolutions in any case require Israel to withdraw from all occupied territories.
In 2005, a former Prime Minister who worked to end Syrian dominance of Lebanon was assassinated, for which some accused Syria, others Israel. Demonstrators supported by the West demanded the end of what some consider military occupation by Syria and its undue influence on Lebanon’s government. A 1991 treaty made Syria responsible for Lebanon’s protection.
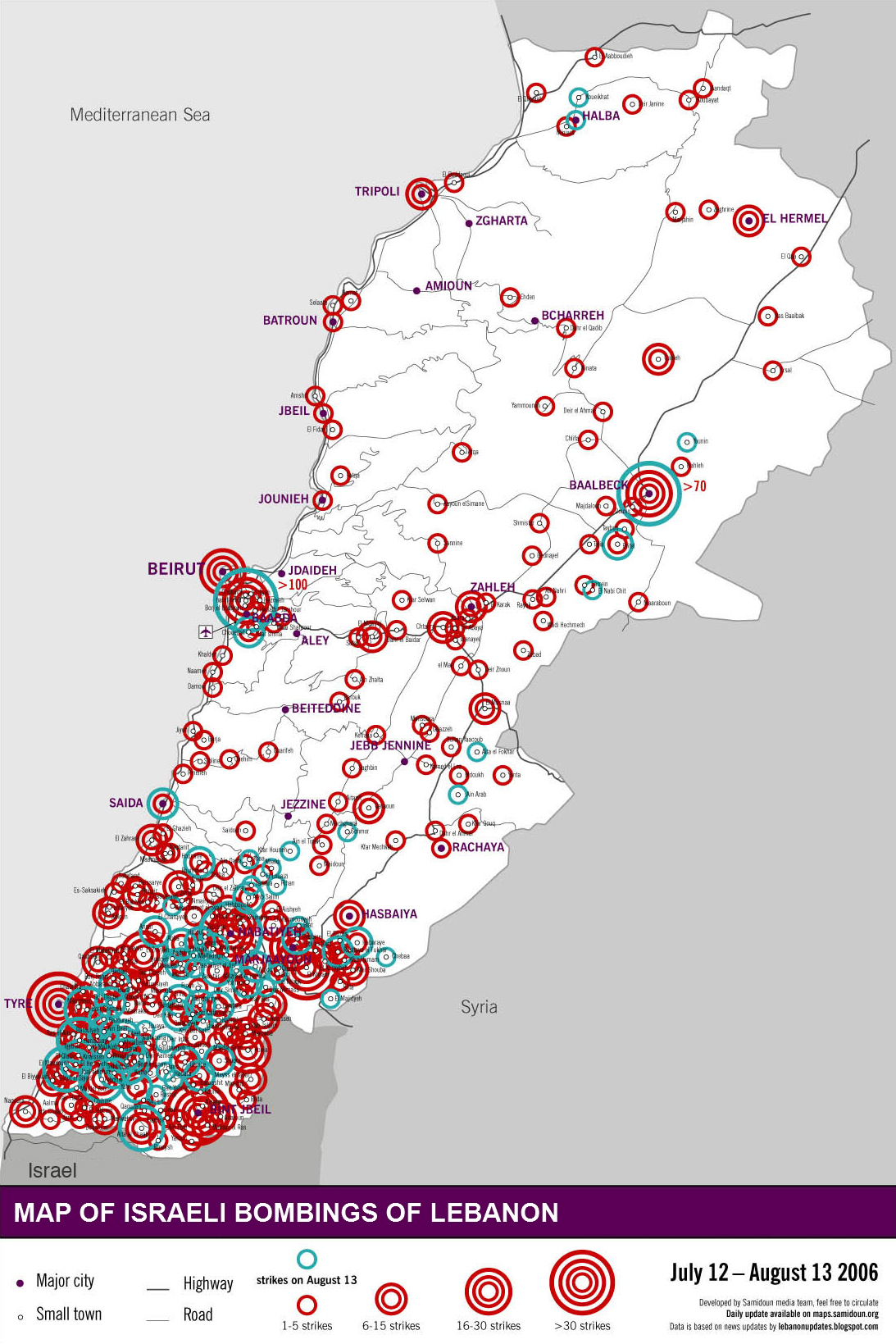
In 2006, Hezbollah launched rocket attacks and raids into Israel. They responded by invading southern Lebanon, and with airstrikes throughout the country that destroyed bridges, ports, power stations, water and sewage treatment plants, schools, hospitals and homes.
The latest threat to Lebanon’s stability is the Syrian civil war. Of Lebanon’s total 5,883,600 population, 450,000 are Palestinian refugees and 1,200,000 are recent Syrian refugees. Refugees make up almost 30% of the population and 20% are very recent arrivals.
Diverse populations are not easily governed even in a democracy.
Most nations in the Middle East are autocracies–Sunni in Saudi Arabia and Jordan, Shia in Iran and Syria, first Sunni now Shia in Iraq. Lebanon is a parliamentary democratic republic a quarter or more of whose population is either Christian, Shia or Sunni citizens, or refugees from Palestine, Jordan and Syria, most them Sunni. That’s a formidable challenge.
And Lebanon’s government was dominated by Syria from 1975 to 2005, while southern Lebanon still is dominated by PLO and Hezbollah forces, which makes it a battle ground with Israel in the quest for a Palestinian nation state.
Lebanon’s future is inextricably tied with Syria, which is in turmoil, Palestine which does not exist as a nation state, and Israel. It seems to have been a mistake to have established Lebanon as an independent nation state and/or not to establish Palestine as one at the same time.